Step by Step Guide to file Income Tax Return in ITR1 format- Tax Planning Strategies
Guide to Filing ITR1 Income Tax Return
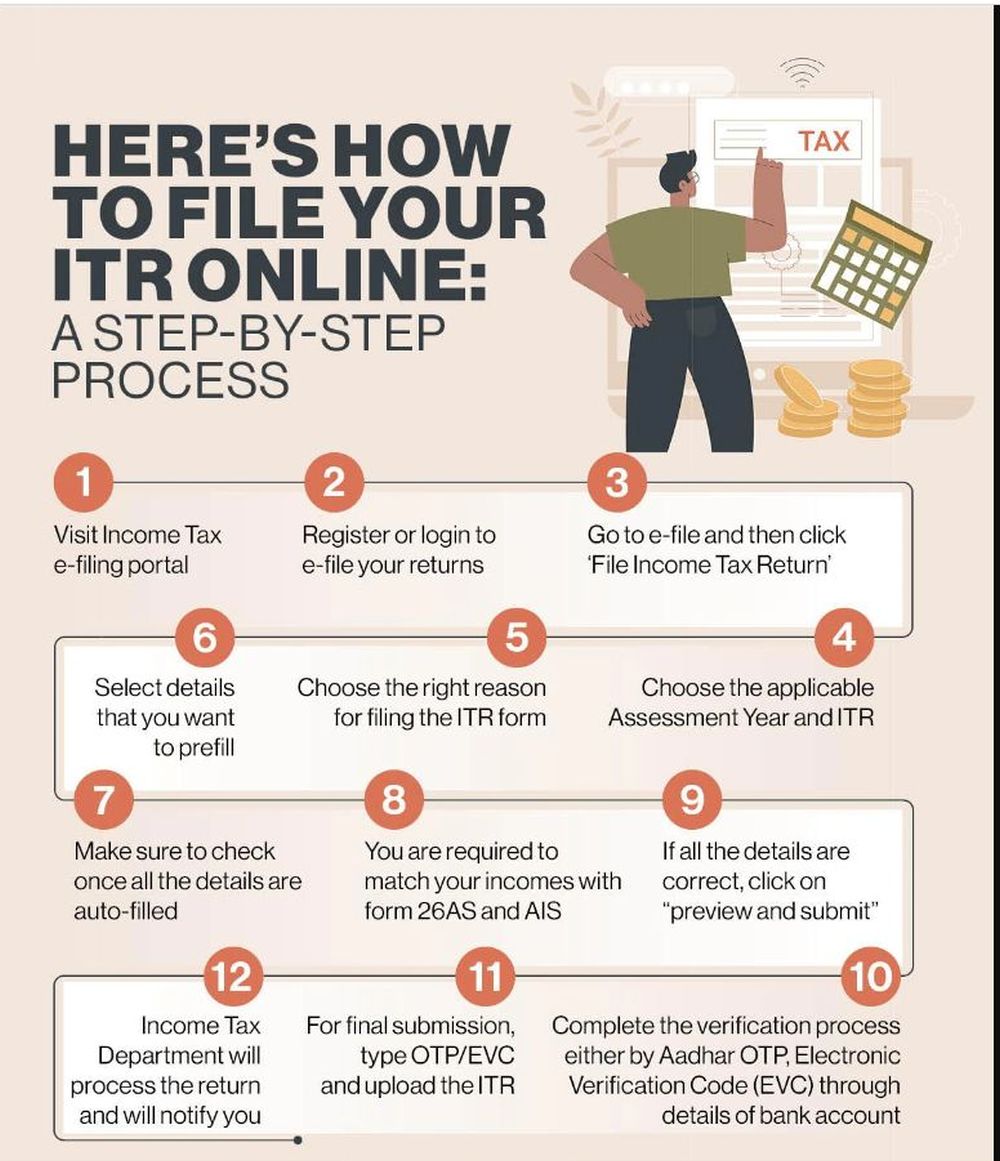
Filing an Income Tax Return (ITR) in India can be done online through the Income Tax Department’s e-filing portal. The ITR1 form is applicable to individuals who have income from salary, one house property, and other sources, excluding income from business or profession. Here is a step-by-step guide to filing ITR1 in India:
Step 1: Gather the required documents.
Before starting the filing process, make sure you have the following documents and information handy:
- PAN (Permanent Account Number)
- Aadhaar card number
- Bank account details (account number, IFSC code)
- Form 16 or salary certificates from your employer
- Details of income from other sources (if any)
- Details of tax-saving investments, if any (such as LIC, PPF, NSC, etc.)
- Bank statements and interest certificates
- TDS certificates (Form 16A) for income other than salary
Step 2: Visit the Income Tax Department’s e-filing portal
Go to the Income Tax Department’s official e-filing portal (https://www(dot) incometax(dot)gov(dot)in/iec/foportal) and register yourself as a new user if you haven’t done so already. If you are already registered, log in using your user ID (PAN) and password.
Step 3: Download the ITR1 form
Once you are logged in, go to the ‘e-File’ tab and select the ‘Income Tax Return’ option. Choose the assessment year for which you want to file the return (e.g., 2023-24) and select the ITR1 form from the options provided. Download the ITR1 form in Excel or Java utility format.
Step 4: Fill in the ITR1 form
Open the downloaded ITR1 form in the appropriate software (Excel or Java utility) and fill in the required details. The form consists of various sections such as personal information, income details, tax computation, and verification. Provide accurate information about your income, deductions, and taxes paid. Ensure that you have all the necessary supporting documents to cross-verify the details.
Step 5: Validate the form
After filling in the form, click on the ‘Validate’ button to check for any errors or missing information. The software will perform an inbuilt validation to identify any inconsistencies or discrepancies. If any errors are found, rectify them before proceeding.
Step 6: Generate the XML file
Once the form is validated successfully, click on the ‘Generate XML’ button. This will create an XML file of your ITR1 form, which is the format accepted by the Income Tax Department’s e-filing portal.
Step 7: Upload the XML file
Go back to the Income Tax Department’s e-filing portal and log in again if required. Under the ‘e-File’ tab, select ‘Income Tax Return’ and choose the appropriate assessment year. Select the ‘Upload XML’ option and browse for the XML file generated in the previous step. Upload the file and wait for the portal to process it.
Step 8: Verify your Return
After the XML file is uploaded, you will be redirected to the verification page. You can choose to verify your return using Electronic Verification Code (EVC) or through Aadhaar OTP, or by sending a signed physical copy of the ITR-V to the Income Tax Department’s CPC (Centralized Processing Centre) within 30 days of e-filing.
What are likely problems that can come up while filing ITR1 form Online
While filing the ITR1 form online, you may encounter some common problems or challenges. Here are a few likely issues that can arise:
Technical glitches:
Online filing platforms may occasionally experience technical issues, such as slow loading, server errors, or connectivity problems. These issues can disrupt the filing process and may require you to try again later.
Incorrect or missing information:
Providing inaccurate or incomplete information in the ITR1 form can lead to rejection or scrutiny of your return. It is crucial to ensure that all details, such as personal information, income, deductions, and tax calculations, are entered correctly and supported by appropriate documents.
Mismatched Form 26AS, AIS:
Form 26AS is a consolidated tax statement that reflects the taxes deducted at source (TDS) and other tax-related details. It is essential to cross-verify the information in your ITR1 form with Form 26AS and with AIS form to avoid any discrepancies or mismatches.
Issues with digital signatures:
If you choose to digitally sign your ITR1 form, you may encounter problems with the digital signature certificate or the signature validation process. Ensure that you have a valid and compatible digital signature certificate to avoid any issues.
Validation errors:
The e-filing portal performs an inbuilt validation check to identify errors or inconsistencies in the form. These errors can include incorrect PAN or Aadhaar details, invalid bank account information, or missing mandatory fields. It is crucial to carefully review the form and rectify any validation errors.
Unable to retrieve past data:
If you have previously filed ITRs online and need to retrieve past data, there may be challenges in accessing and importing the information into the current ITR1 form. This can happen if there are compatibility issues between the old and new versions of the filing software.
Income from multiple employers:
If you have changed jobs during the financial year and have income from multiple employers, there can be challenges in correctly reporting the details in the ITR1 form. Ensure that you have the necessary Form 16s or salary certificates from each employer to accurately report your income. Please note that ITR1 form is to be used in case of single employer only. In case of multiple employers use ITR2 form.
Difficulty in claiming deductions:
The ITR1 form allows you to claim deductions under various sections of the Income Tax Act. However, understanding and correctly applying the relevant sections can be challenging. It is advisable to consult a tax professional or refer to the Income Tax Act guidelines to ensure proper deduction claims.
Facing any problem in filing ITR? Feel free to mail us for instant solution.
When it comes to tax planning for individuals filing their return in ITR-1 (Sahaj), there are several strategies and tips you can consider to optimize your tax liability. Here are some useful tips:
Utilize deductions under Section 80C:
Make the most of deductions available under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act. Invest in tax-saving instruments such as Public Provident Fund (PPF), Employee Provident Fund (EPF), National Savings Certificates (NSC), tax-saving fixed deposits, etc. You can claim deductions of up to Rs. 1.5 lakh under this section.
House Rent Allowance (HRA):
If you are a salaried individual and receive HRA as part of your salary, ensure you claim the HRA exemption. The amount exempted depends on the actual HRA received, rent paid, and the city of residence.
Medical insurance premium:
Claim deductions for the premium paid towards medical insurance policies for yourself, your spouse, children, and parents. Under Section 80D, you can claim deductions up to Rs. 25,000 (Rs. 50,000 for senior citizens) for medical insurance premium payments.
Interest on home loan:
If you have taken a home loan, you can claim deductions on the interest paid under Section 24(b). The maximum deduction allowed is Rs. 2 lakh per year for self-occupied properties.
Donation to charitable institutions:
Donations made to eligible charitable institutions or funds qualify for deductions under Section 80G. Ensure that the organization you donate to is approved by the government and issues a valid donation receipt.
Capital gains:
If you have incurred capital gains from the sale of assets such as stocks, mutual funds, or property, make use of exemptions available under Section 54 or Section 54F to reduce your tax liability. Please note if you have any Capital Gains, you need to file return in some other form as ITR2 or ITR3 and not in ITR1.
Maintain proper documentation:
Keep all necessary documents such as investment proofs, rent receipts, medical bills, donation receipts, home loan interest certificate, etc., as supporting evidence for your deductions and exemptions.
Remember, tax planning should be done in accordance with the prevailing tax laws and regulations. It is advisable to consult a qualified tax professional or chartered accountant for personalized advice based on your specific financial situation.
What are likely issues if you file return yourself without help of professional
Filing your tax return without the help of a professional can have several potential issues. While many individuals are able to successfully file their own taxes, it’s important to be aware of the challenges involved. Here are some common issues that can arise when filing a return without professional assistance:
Errors:
Tax laws and regulations can be complex, and one is likely to make mistakes when preparing your return. Errors can lead to underpayment or overpayment of taxes, which may result in penalties, interest charges, or delays in receiving any refund you’re owed.
Missed deductions and credits:
Without a thorough understanding of tax laws, you may overlook certain deductions or credits that could reduce your tax liability or increase your refund. Tax professionals are knowledgeable about the various deductions and credits available and can help ensure you’re taking advantage of all applicable ones.
Lack of expertise:
Tax professionals undergo extensive training and stay updated on changes in tax laws. They possess specialized knowledge that allows them to navigate complex tax situations, such as self-employment income, rental properties, investments, or international tax obligations. Filing without professional assistance could lead to incorrect reporting and potential audit triggers.
Scrutiny risk:
Although the risk of being Scrutinized is relatively low for most individuals, certain red flags or errors on your return can increase the likelihood of an Scrutiny. A tax professional can help minimize audit risks by ensuring accurate reporting and compliance with relevant tax laws.
Time-consuming:
Preparing your own tax return can be time-consuming, especially if you’re not familiar with the process or have complex financial situations. Hiring a professional can save you time and allow you to focus on other important aspects of your life.
Limited support:
When you file on your own, you may not have access to professional advice or assistance if you encounter any issues or questions during the process. Hiring a tax professional provides you with access to guidance and support, which can be particularly helpful if you face an audit or need to navigate complex tax matters.
It’s important to note that many individuals are capable of successfully filing their own tax returns, especially if their financial situation is relatively straightforward. However, if you have complex financial affairs, are unsure about certain tax laws, or simply prefer the peace of mind that comes with professional assistance.


 ITAT Amritsar: No Section 269SS Violation for One-Time Cash Payment Before Sub-Registrar
ITAT Amritsar: No Section 269SS Violation for One-Time Cash Payment Before Sub-Registrar  Tax Officials Unleash Digital Dragnet: How New Raid Powers Redefine Privacy, Property Rights in India and likely to Fuel Corruption
Tax Officials Unleash Digital Dragnet: How New Raid Powers Redefine Privacy, Property Rights in India and likely to Fuel Corruption  Income Tax Department Rewards for Reporting Tax Evasion: A Comprehensive Guide
Income Tax Department Rewards for Reporting Tax Evasion: A Comprehensive Guide  Forfeiture of Gratuity by Employer- What are the Remedies for an employee- Can employer be challenged?
Forfeiture of Gratuity by Employer- What are the Remedies for an employee- Can employer be challenged?  Employer can forfeit gratuity of an employee in case of moral turpitude
Employer can forfeit gratuity of an employee in case of moral turpitude  Diving Deeper: The Impact of the New Tax Bill on Dairy and Farming Income
Diving Deeper: The Impact of the New Tax Bill on Dairy and Farming Income