Receiving a gift of more than Rupees 50,000 could be a tax trap
 Receiving a gift more than rupees 50,000/- is taxable under the current tax regulations. The Indian gift tax Act was constituted on April 01, 1958 effected all over the country except Jammu and Kashmir. As per the gift tax Act 1958, gifts above of Rs. 25,000/- by cash, draft, check or others received from non-blood relations were taxable. With effect from October 01, 1998, existing gift tax Act has been abolished and any gifts made on or after the date were tax-free.
Receiving a gift more than rupees 50,000/- is taxable under the current tax regulations. The Indian gift tax Act was constituted on April 01, 1958 effected all over the country except Jammu and Kashmir. As per the gift tax Act 1958, gifts above of Rs. 25,000/- by cash, draft, check or others received from non-blood relations were taxable. With effect from October 01, 1998, existing gift tax Act has been abolished and any gifts made on or after the date were tax-free.
Again in the year 2004 the Act was reintroduced (Effective from assessment year 2005-2006) and a new provision was introduced in the Income Tax Act 1961 under section 56(2). As per the new provision introduced in the Act, the gifts received by any individual or Hindu Undivided Family (HUF) more than Rs.50, 000/- in a year would be taxable. The present revised provisions in the Income Tax Act are applicable to the state of Jammu & Kashmir as well.
Provisions of the Act
The provision under the Act says that any gift received in excess of Rs. 50,000/- by form of cash, demand draft, cheque or immovable assets by an individual or Hindu Undivided Family is taxable. For further clarity the provision under the Act can be explained further. Suppose a friend or relative gives a gift worth Rs. 45,000/- which is not taxable. But if another friend or relative gives another Rs.6000/-, the full amount of Rs.51, 000/- received as gift will be taxable.
It is very important to keep in mind that the gift tax is considered not only on cash received but even on gift received in kind such as immovable property including land, building etc and movable property like jewellery, paintings, shares, debentures, archeological collections etc.;. The gift tax is applicable to the done only not the donor.
Definitions of Gift
“Gift” means the transfer of any kind of existing movable or immovable property made voluntarily and without consideration in money or anything worth equivalent to the items transferred. The definition can be further simplified that, giving something willingly or voluntarily without receiving payment, just to show goodwill to someone, to honor or to make a gesture of help.
Gifts can be received from whom
According to the Gift Tax Act, individuals can receive gifts from blood relatives, at the time of marriage, as inheritance and in consideration of death of blood relatives. Under section 56(2)(vi) of the Income Tax Act, the definition of the term ‘relative’ is recorded various relations only with reference to an individual.
Who is considered as a relative?
As per the IT Act, the spouse (husband or wife), sisters, brothers, sisters in-law, brothers in-law, parents, parents in-law, lineal ascendants or descendants of the individual or spouse, and sisters and brothers of parents of individual spouse are considered as relatives.

 Can an assessee pay House Rent to his parents and claim relief? Would there be any legal complications?
Can an assessee pay House Rent to his parents and claim relief? Would there be any legal complications?  Boost Your Business & Reduce Taxes: A Guide to Maximizing Benefits Under Section 80JJAA
Boost Your Business & Reduce Taxes: A Guide to Maximizing Benefits Under Section 80JJAA 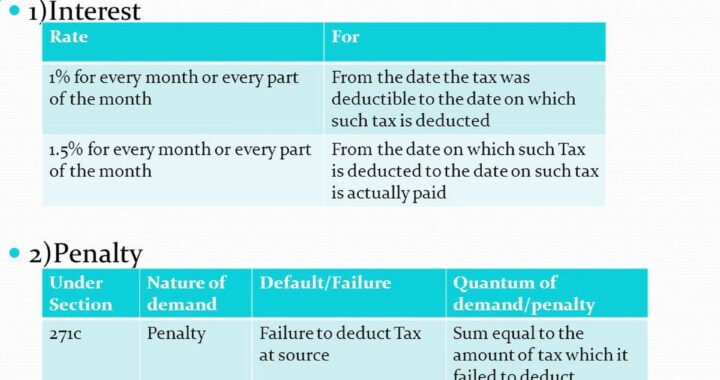 What is remedy to taxpayer if the Tax deductor fails to deposit the TDS or fails to file TDS Return
What is remedy to taxpayer if the Tax deductor fails to deposit the TDS or fails to file TDS Return  What is Income Tax Liability on Income from trading in Future and Options
What is Income Tax Liability on Income from trading in Future and Options  The Importance of Filing Your Income Tax Return on Time: A Financial Must-Do
The Importance of Filing Your Income Tax Return on Time: A Financial Must-Do  Is Addition made by Assessing officer on basis of mismatch between AIR and F26AS Justified
Is Addition made by Assessing officer on basis of mismatch between AIR and F26AS Justified  Major Changes Expected in Direct Tax Code 2025 and why these matter
Major Changes Expected in Direct Tax Code 2025 and why these matter